 +86 755 2794 4155
+86 755 2794 4155  sales@knownpcb.com
sales@knownpcb.com
-
Shenzhen KNOWNPCB Technology Co., Ltd.
 +86 755 2794 4155
+86 755 2794 4155  sales@knownpcb.com
sales@knownpcb.com
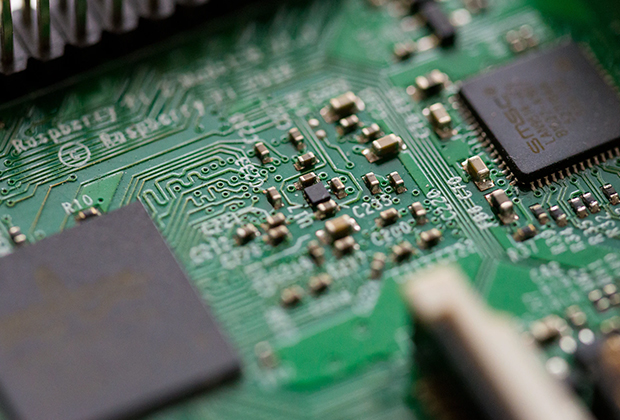
Have you noticed that now more and more of our lighting is using led lighting.What is LED? Compared to the traditional light bulbs, LEDs have lower power consumption, longer lifetime and higher energy efficiency. In the PCB industry,when we say LED PCB, it refers to the pcb used for LED lighting, if you are looking for a suitable LED PCB for your lighting system, this article may bring you something. WHAT ARE LEDS COMPOSED OF?LED is an initial light-emitting diode that produces light when an electric current passes through. LEDs typically have negative and positive electrodes, which generate light in the visible light region.The LEDS are glued to the PCB by soldering process and have electrical connections for lighting.Since light-emitting diodes dissipate a lot of heat when they are in use, when you are designing LED, the metal core is usually the best choice for LED PCB, it is because that it dissipates heat more faster. Among them, the metal material aluminum is the most widely used
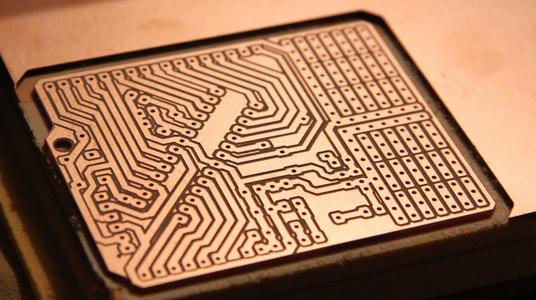
The resistance encountered during the propagation of high-frequency signals or electromagnetic waves in electronic device transmission signal lines is called "impedance". Why do some boards require impedance during the production process, and what are the advantages of impedance PCB circuit boards! 1. It is necessary to consider the installation of electronic components through plug connections, and later SMT patch connections also need to consider issues such as conductivity and signal transmission performance, so the lower the impedance, the better. 2. During the production process, the materials used must have low electrical resistivity to ensure that the overall impedance value of the circuit board meets the product quality requirements and can operate normally. 3. PCB tin plating is the most common problem in the production of the entire circuit board, and it is a key link that affects impedance; Its biggest defects are easy oxidation or deliquescence, poor solderability, mak
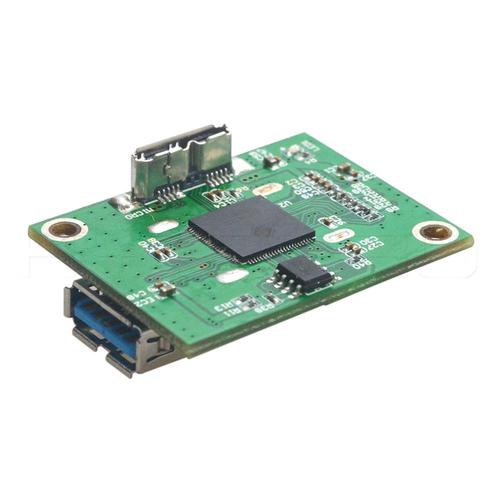

The origin of PCB circuit board printing in China probably dates back to the middle and late 1990s. The research on automatic optical detection systems for circuit board printing defects is still at a relatively early level. With the continuous maturity of process technology in the later stage, there has been progress in express delivery in the field of printed circuit boards. With the rapid development of the electronics industry, the application scope of circuit boards has also increased, So how do we distinguish the quality and sincerity of finished circuit boards! 1: Board thickness control standards: Different factories have limited printable process capabilities when printing circuit boards. The standard accuracy of the manufacturer can be determined based on the board thickness. The smaller the control tolerance, the stronger the printing ability, while the larger the control tolerance, the smaller the printing ability. 2: The glossiness of the solder mask color on the boa
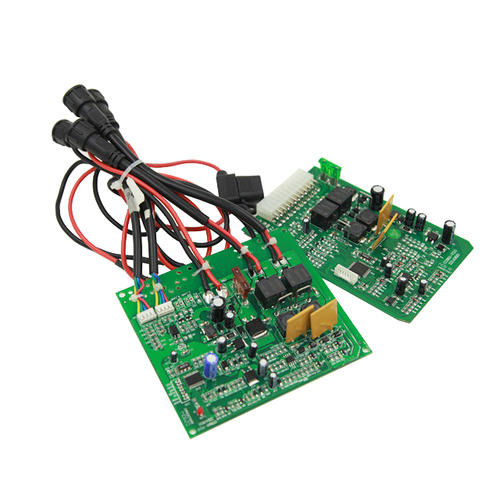

The shape of circuit board pads can be divided into 7 categories: 1. Square solder pads: commonly used when the components on a printed circuit board are large but few, and the printed wires are simple. 2. Circular solder pads: widely used in single and double-sided printed boards with regular component arrangement. 3. Island pad: The connection between pads is integrated and is commonly used in vertical irregular arrangement installation. 4. Teardrop solder pads: often used when connecting thin wires, commonly used in high-frequency circuits. 5. Polygonal pads: Used to distinguish pads with similar outer diameters but different apertures, making it easy to process and assemble. 6. Elliptical pad: This type of pad has sufficient area to enhance peel resistance and is commonly used in dual inline devices. 7. Open solder pads: commonly used to ensure that the holes of manually repaired solder pads are not sealed by solder after wave soldering.
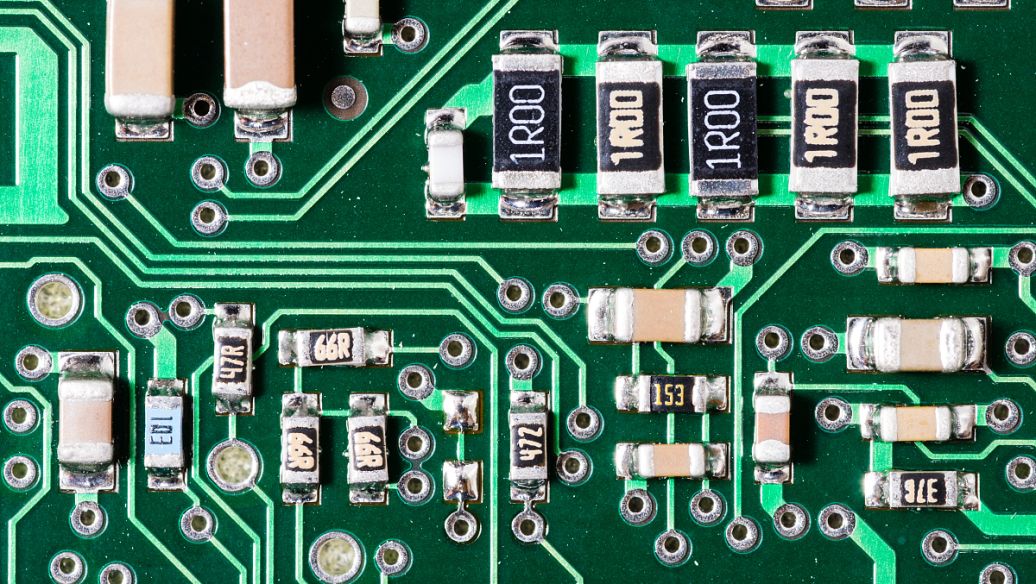
1. The minimum diameter on one side of all solder pads shall not be less than 0.25mm, and the maximum diameter of the entire solder pad shall not exceed three times the aperture of the component. 2. Efforts should be made to ensure that the distance between the edges of two solder pads is greater than 0.4mm. 3. In cases of dense wiring, it is recommended to use elliptical and elongated solder pads. 4. For plug-in components, in order to avoid copper foil breakage during welding, the single-sided connecting plate should be completely covered with copper foil, and the minimum requirement for double panels should be to fill in tears. 5. All machine insertion parts should be designed as drip solder pads along the bending direction to ensure full solder joints at the bending position. 6. Daisy shaped solder pads should be used on large-area copper sheets to avoid virtual soldering.
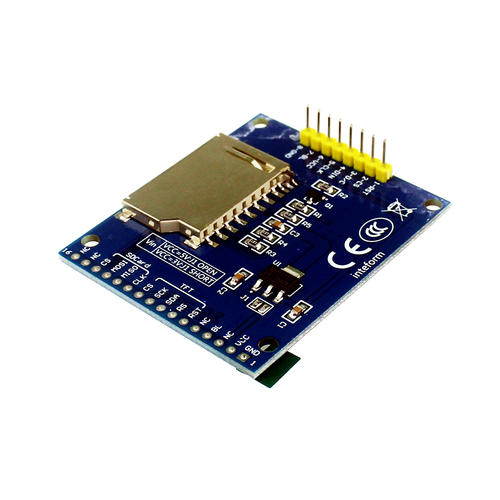
(1) Protective post-treatment Except for chrome plating, all other protective coatings used as surface coatings must undergo appropriate post-treatment to maintain or enhance their protective performance. The most commonly used post-processing method is passivation. For those with high protection requirements, surface coating treatment should be carried out, such as glossy coating treatment. From the perspective of environmental protection and cost, water-based transparent coating can be used. (2) Decorative post-treatment Decorative post-treatment is a common treatment process in non-metallic electroplating. For example, imitation gold, imitation silver, imitation antique copper plating, brushing, coloring or dyeing, and other artistic treatments. Most of these treatments also require the surface to be coated with transparent gloss coating. Sometimes it is necessary to use colored transparent coatings, such as imitation gold, red, green, purple and other colors. (3) Functional
1、 Decanting method Decanting method is actually a filtration method, which is a physical method in the wastewater treatment of PCB board industry. The flushing water containing copper shavings discharged by the deburring machine can be filtered and removed after being treated by a decanter. The effluent filtered by the decanter can be reused as cleaning water from the burr machine. 2、 Chemical method Chemical methods include redox method and chemical precipitation method. The oxidation-reduction method is the use of oxidants or reducing agents to convert harmful substances into harmless or easily precipitated substances. The cyanide containing wastewater and chromium containing wastewater in circuit boards are often treated using the oxidation-reduction method, as explained later. Chemical precipitation method is the use of one or several chemical agents to convert harmful substances into easily separable precipitates or precipitates. There are various chemical agents used for
1. The solderability of circuit board holes affects welding quality Poor solderability of circuit board holes will result in virtual soldering defects, affecting the parameters of components in the circuit, leading to unstable conduction of multi-layer board components and inner wires, and causing the entire circuit function to fail. The so-called weldability refers to the property of the metal surface being wetted by molten solder, that is, the formation of a relatively uniform and continuous smooth attached film on the metal surface where the solder is located. The main factors affecting the solderability of printed circuit boards are: (1) the composition of the solder and the properties of the soldered material. Solder is an important component of the welding chemical treatment process, which is composed of chemical materials containing flux. The commonly used low melting point eutectic metals are Sn-Pb or Sn-Pb-Ag. The impurity content should be controlled in a certain proport
PCB wastewater is polychlorinated biphenyl wastewater, which is a type of wastewater in the printing industry and circuit board factories. Nowadays, the world produces 300 million to 400 million tons of toxic and harmful chemical waste annually, among which persistent organic pollutants (POPs) are of great ecological harm and the most widely spread on Earth. In addition, PCB wastewater is divided into cleaning wastewater, ink wastewater, complexation wastewater, concentrated acid wastewater, concentrated alkali wastewater, etc. The production of printed circuit boards (PCBs) requires a large amount of water, and there are many types of pollutants in the wastewater with complex components. Reasonable classification, collection, and treatment of wastewater based on the characteristics of different PCB manufacturers are key to ensuring that wastewater treatment meets standards. For the treatment of wastewater in the PCB board industry, there are chemical methods (chemical precipitatio
Inquiry Now

