 +86 755 2794 4155
+86 755 2794 4155  sales@knownpcb.com
sales@knownpcb.com
-
Shenzhen KNOWNPCB Technology Co., Ltd.
 +86 755 2794 4155
+86 755 2794 4155  sales@knownpcb.com
sales@knownpcb.com

Master advanced PCB processes: A technical guide to Countersinks, Plated Half-Holes (Castellation), Edge Plating, and IPC Type 7 Resin Via Filling for high-density designs.

Explore the 15 complete steps of the PCB manufacturing process. From Cutting and Lamination to AOI and Final Testing, see how we build high-quality printed circuit boards. Click for the full guide.

Learn how PCB flammability ratings and CTI index impact product safety. Discover how KNOWNPCB ensures UL94 V-0 certified, high-reliability PCB manufacturing.

Advanced technology in HDI multilayer PCB meeted the challenge of AI Server | KNOWN PCB

t focuses only on the three main surface finishes — HASL, ENIG, and Hard Gold — and emphasizes the comparative sections (HASL vs ENIG, ENIG vs Hard Gold).

Discover essential PCB terminology with clear explanations of substrates, vias, surface finishes and so on.

Learn about different PCB types and their applications. Explore PCB classification by layers, materials, and specialized functions for modern electronics.
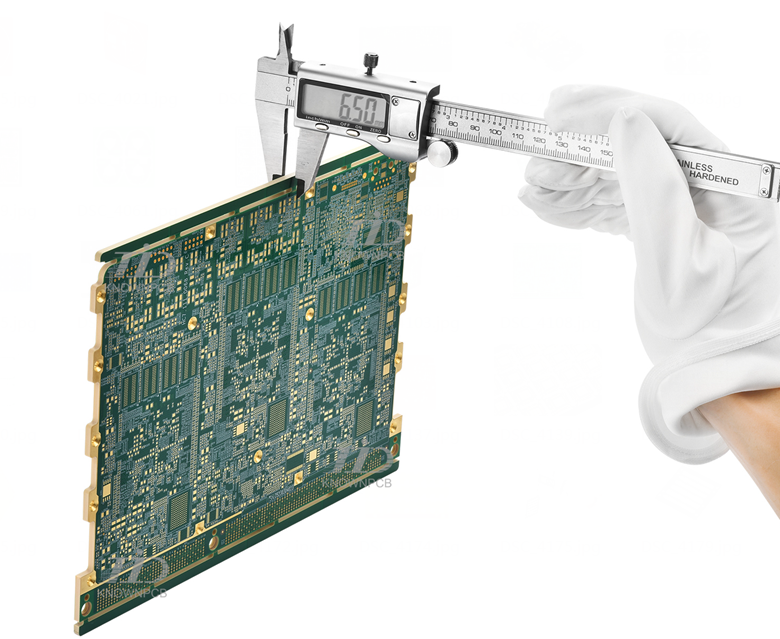
Printed Circuit Board (PCB), hailed as the "mother of electronic products," serves as the foundation of modern electronic devices. It is not only a mounting platform for electronic components but also the key to achieving electrical connections. Almost all electronic devices, from consumer electronics to aerospace systems, rely on PCBs to function.
In electronics manufacturing, the quality of a single solder joint can determine the reliability of an entire circuit board. Even the smallest defect can cause a device to fail at a critical moment, or worse, lead to an entire batch of products being scrapped. In this article, we’ll explore 14 of the most common PCB soldering defects, along with their hazards and causes.
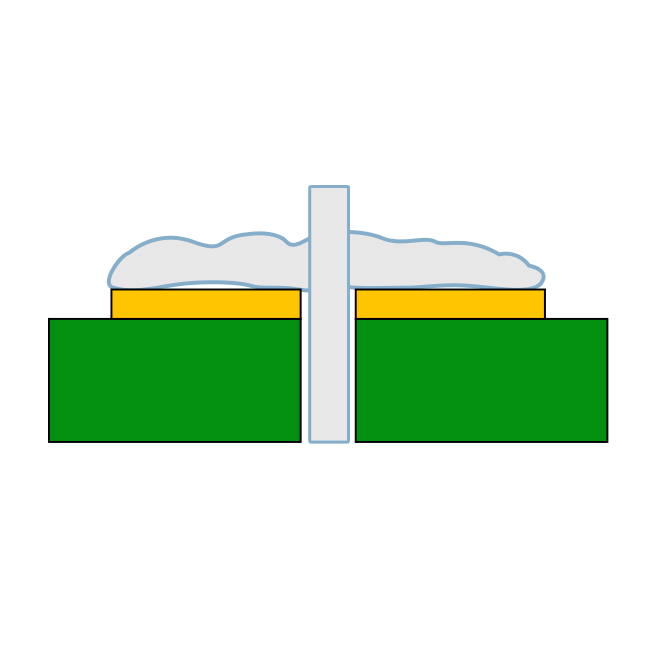
According to the IPC-A-610 standard,Blistering is a form of delamination characterized by localized swelling and separation between any layers of the laminated base material, or between the base material and the conductive foil or protective coatings. Delamination refers to the separation that occurs between layers of the base material, between the base material and conductive foil, or between other internal interfaces within the PCB.

In the field of modern identification and information storage, QR Code and Data Matrix (DM) are two core 2D barcode technologies. To intuitively present their characteristic differences, we will compare them from three dimensions: appearance & structure, data capacity, and usage advantages.
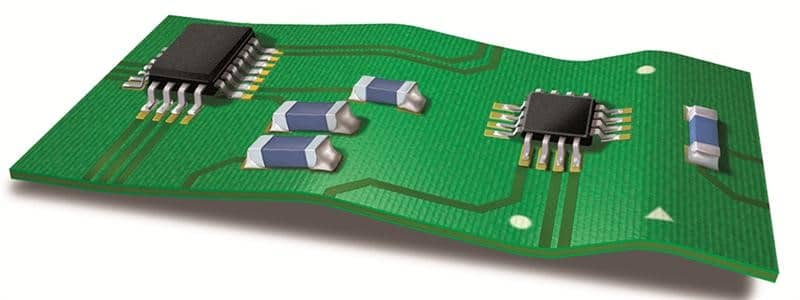
Warpage refers to the phenomenon that the plane of the PCB is bent or deformed due to various reasons during the manufacturing, storage or use of the PCB. This deformation may be local or overall, and is usually manifested as the PCB no longer remaining flat.
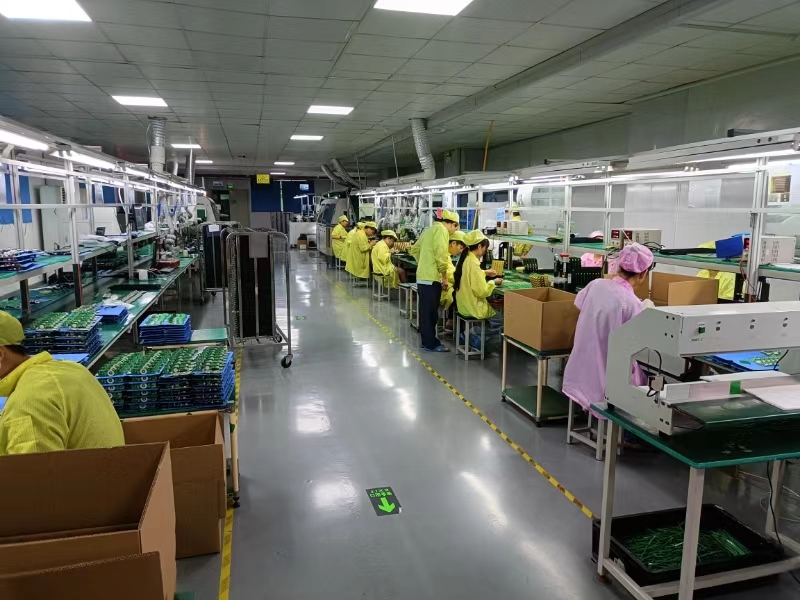

KnownPCB provides one-stop PCB and PCBA solution from PCB design, DFMA analysis, PCB manufacturing, SMT placement, to terminal DIP plug-ins.No Min.Qty's required.
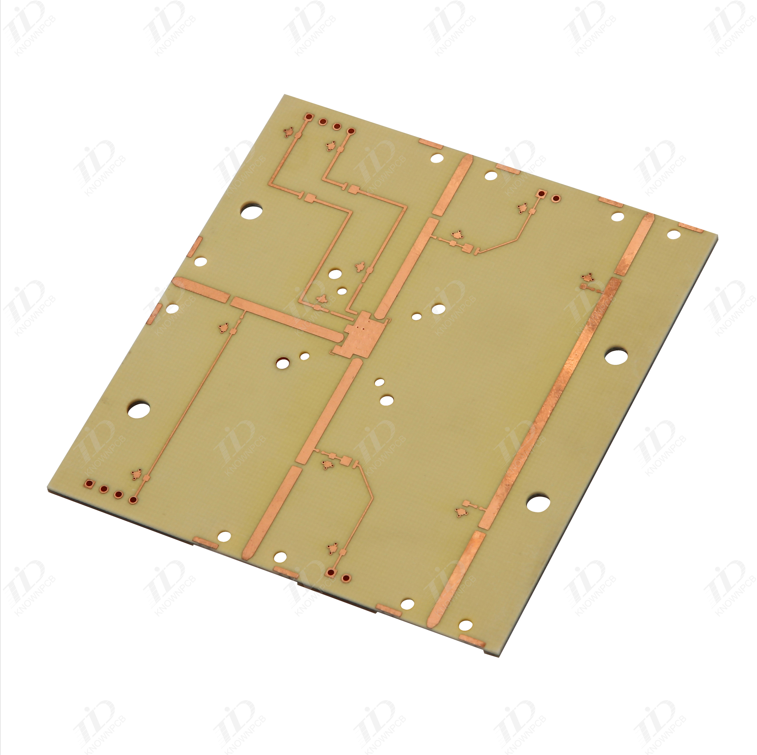
With the rapid advancement of electronic communication technology, the demand for high-frequency circuit boards in communication equipment has significantly increased to support high-speed and high-frequency signal transmission. These boards utilize dielectric materials that exhibit exceptional electrical properties and outstanding chemical stability.
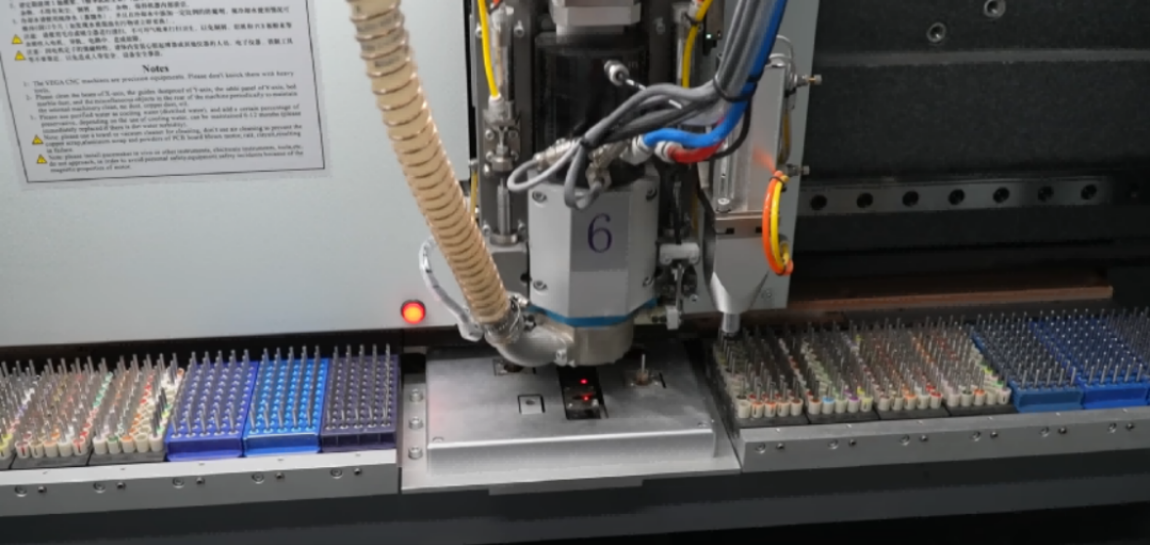

Drilling of PCB board is one of the crucial processes in PCB manufacturing, and the quality of this drilling directly affects the performance and reliability of the entire PCB board.Next, let's discuss some of the key factors that affect the drilling quality of PCB boards.
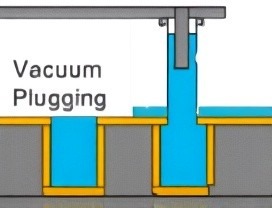
Resin plugging is a process that fills vias or through-holes with insulating resin, then cures it to create a flat, sealed surface. This enhances layer bonding, supports high-density interconnects, and improves reliability.Compared to solder mask plugging, resin ensures better sealing and thermal stability.
Aging tests for printed circuit boards (PCBs) are essential procedures aimed at evaluating the long - term reliability and performance of PCBs under various stress conditions. These tests simulate the effects of extended usage, environmental factors, and electrical loads that PCBs may encounter during their operational life, helping manufacturers and engineers identify potential failures and improve product quality. One of the most common aging test methods is thermal aging. In this method, PCBs are exposed to elevated temperatures for an extended period. Typically, the temperature is set well above the normal operating temperature, often ranging from 85°C to 150°C, depending on the application and the materials used in the PCB. The high - temperature environment accelerates the degradation processes within the PCB, such as the oxidation of metal traces, the deterioration of solder joints, and the thermal expansion and contraction of different materials. By monitoring the PCB'
High-Density Interconnector (HDI) PCBs are advanced printed circuit boards characterized by a higher wiring density per unit area compared to standard PCBs. They incorporate fine lines, microvias, and often multiple layers, which allow for more compact and efficient designs.
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) impedance testing is a critical process in PCB design and manufacturing, playing a fundamental role in ensuring the reliable operation of electronic circuits. Impedance refers to the opposition that a circuit presents to the flow of alternating current (AC), and it is a key parameter that affects signal integrity in high - speed digital and analog circuits. In high - speed digital circuits, maintaining proper impedance control is essential. As data transfer rates increase, signals travel at higher frequencies, and factors such as signal reflections, crosstalk, and attenuation become more pronounced. If the impedance of the PCB traces is not properly matched to the impedance of the connected components (such as integrated circuits), signal reflections occur when the signal reaches the end of the trace or encounters a change in impedance. These reflections can cause the signal to distort, resulting in errors in data transmission, such as bit - errors in d
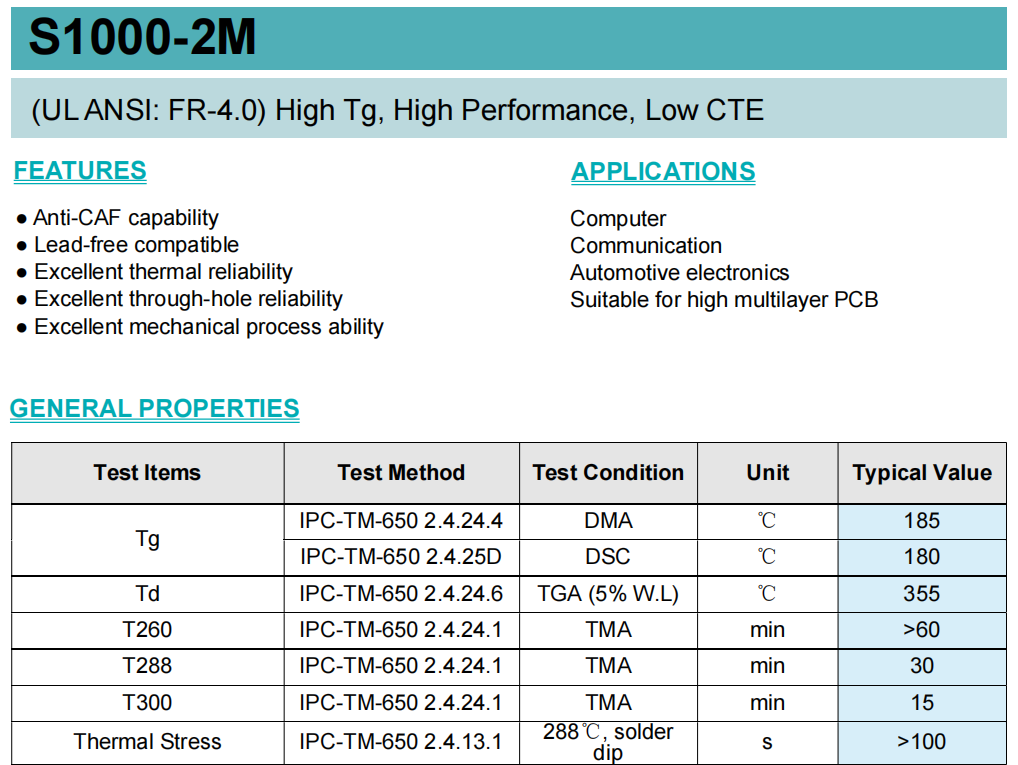
Relationship between PCB high-TG materials and copper foilUnderstanding Glass Transition Temperature(TG ) The glass transition temperature of a PCB board is a key indicator for measuring its performance. When the temperature rises to a certain level, the PCB substrate will transition from a "glass state" to a "rubber state". The higher the TG value, the better the temperature resistance of the PCB, and its performance such as heat resistance, moisture resistance, chemical resistance, and resistance stability is also better.The distinction between standard FR-4 and high-Tg FR-4 In the hot state, especially when heated after moisture absorption, there are differences in the mechanical strength, dimensional stability, adhesion, water absorption, thermal decomposition, thermal expansion, and other aspects of the material. High-Tg FR-4 substrates demonstrate superior performance across these critical parameters compared to standard-Tg counterparts.Why can't standard-Tg and h
Inquiry Now

