 +86 755 2794 4155
+86 755 2794 4155  sales@knownpcb.com
sales@knownpcb.com
-
Shenzhen KNOWNPCB Technology Co., Ltd.
 +86 755 2794 4155
+86 755 2794 4155  sales@knownpcb.com
sales@knownpcb.com
 2025-02-26
2025-02-26
 848
848
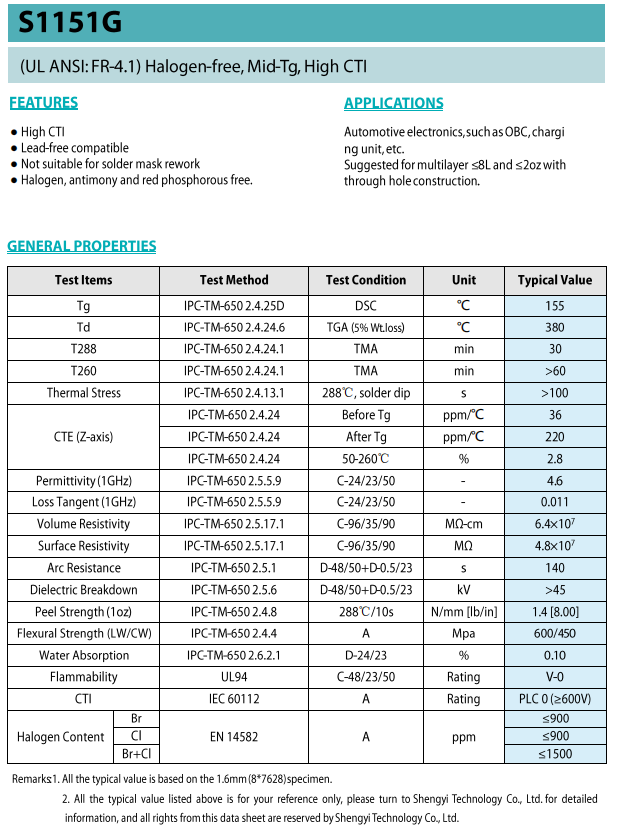
Halogen free boards are environmentally friendly materials, and the substrates used for halogen-free circuit boards are processed from halogen-free raw materials.
Electronic devices contain specific materials that contain the highest concentration of halogens. To create a halogen-free circuit board on its printed circuit board, it is necessary to replace some materials or reduce their usage, and also determine the halogen-free content of the circuit. Some substitute materials have special design requirements, which ultimately need to be considered.
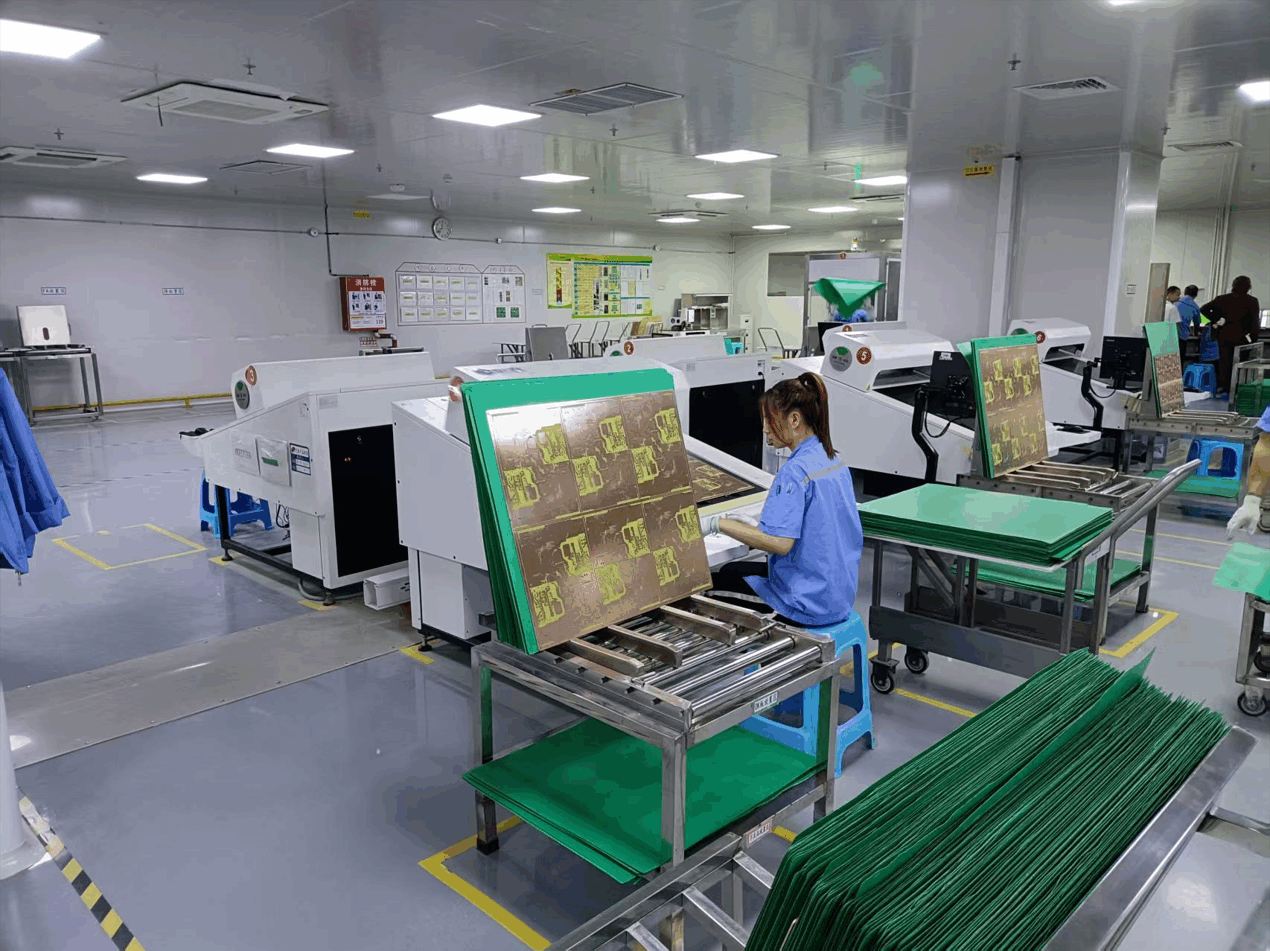

The vast majority of halogen-free boards are mainly composed of phosphorus and phosphorus nitrogen series
Phosphorus containing resin decomposes into polyphosphoric acid during combustion, which has strong dehydration properties and forms a carbonized film on the surface of the polymer resin, isolating the burning surface of the resin from contact with air and extinguishing the fire to achieve flame retardant effect.
Polymer resins containing phosphorus and nitrogen compounds produce non combustible gases during combustion, which assist in flame retardancy of the resin system.
What are the characteristics of halogen-free board?
•Insulation properties
Due to the use of P or N to replace halogen atoms, the polarity of the molecular bond segments of epoxy resin is reduced to some extent, thereby improving insulation resistance and resistance to breakdown.
•Water absorption
Halogen free board materials have lower water absorption compared to conventional halogen flame retardant materials due to the fact that N and P in nitrogen phosphorus based oxygen reducing resins have fewer electrons compared to halogens, and their probability of forming hydrogen bonds with hydrogen atoms in water is lower than that of halogen materials. For sheet metal, low water absorption has a certain impact on improving the reliability and stability of the material.
•Thermal stability
The nitrogen and phosphorus content in halogen-free sheets is higher than that in ordinary halogen materials, resulting in an increase in both the monomer molecular weight and Tg value. Under heat, the molecular mobility of halogen-free materials will be lower than that of conventional epoxy resins, resulting in a relatively lower coefficient of thermal expansion.
The demand for halogen-free materials is increasing
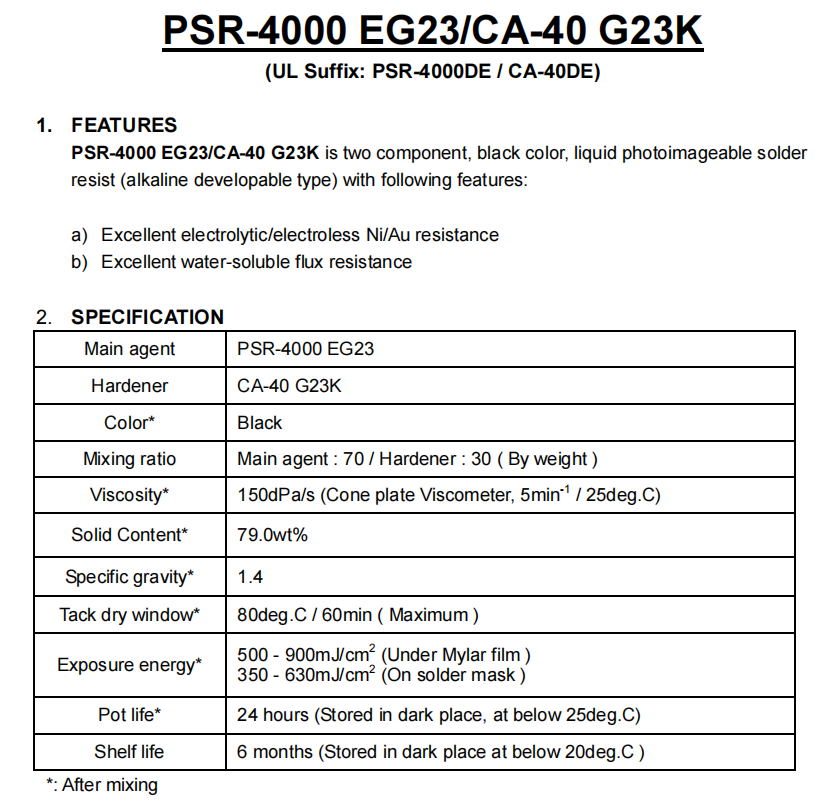
Compared to halogenated sheets, halogen-free sheets have more advantages, and replacing halogenated sheets with halogen-free sheets is also a trend. There are many types of halogen-free solder mask inks currently available on the market, and their performance is not much different from ordinary liquid photosensitive inks. The specific operation is also basically similar to ordinary inks.
Halogen free circuit boards typically have good heat dissipation and reliability, making them suitable for high-temperature processes required for lead-free circuits. Also, due to its low dielectric constant, it can maintain signal integrity. So the demand for halogen-free circuit boards has been increasing.

Or call +86 755 2794 4155
Inquiry Now

