 +86 755 2794 4155
+86 755 2794 4155  sales@knownpcb.com
sales@knownpcb.com
-
Shenzhen KNOWNPCB Technology Co., Ltd.
 +86 755 2794 4155
+86 755 2794 4155  sales@knownpcb.com
sales@knownpcb.com
 2025-04-10
2025-04-10
 988
988
Material Costs
The choice of substrate material (e.g., FR-4, high-frequency materials) significantly impacts costs. Specialty materials typically come at a premium.
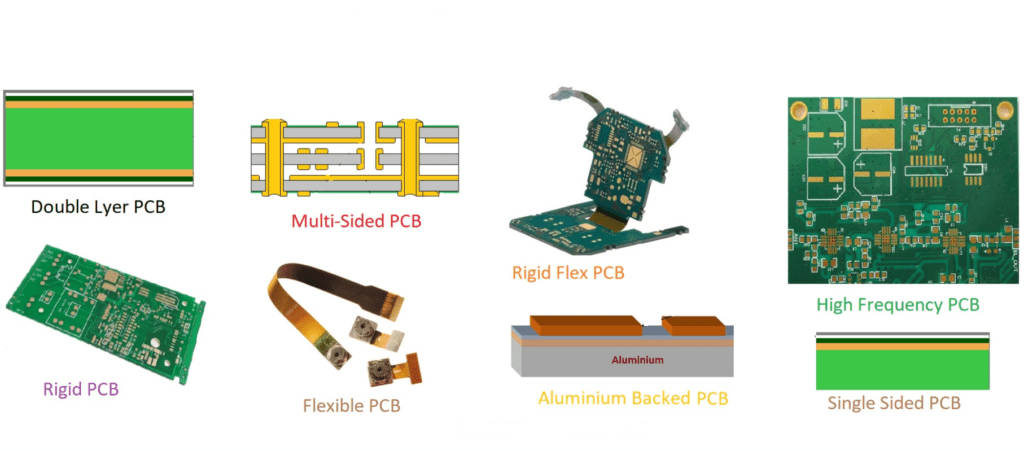
Layer Count
The number of layers in a PCB affects manufacturing complexity and cost. More layers generally lead to higher prices.
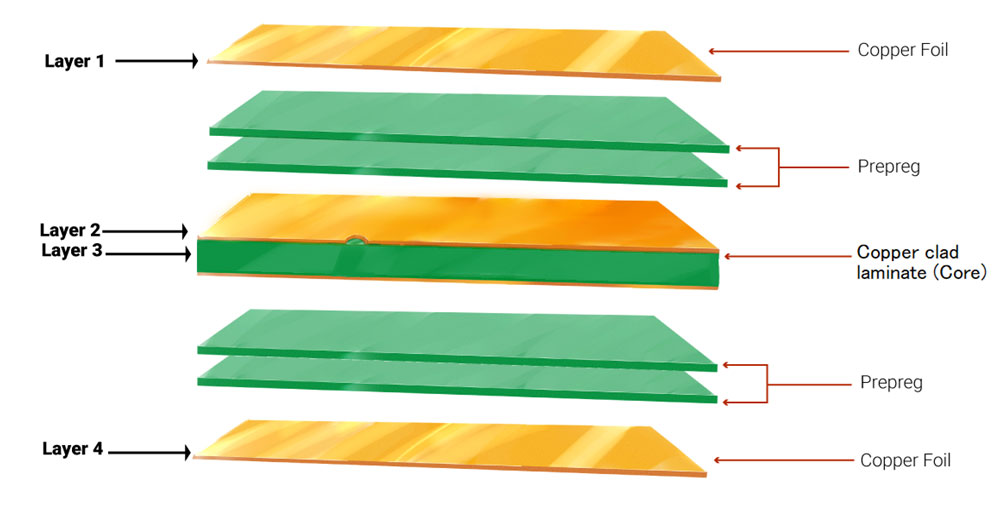
Board Size and Thickness
Larger and thicker boards require more material and may also need specialized handling, increasing costs.
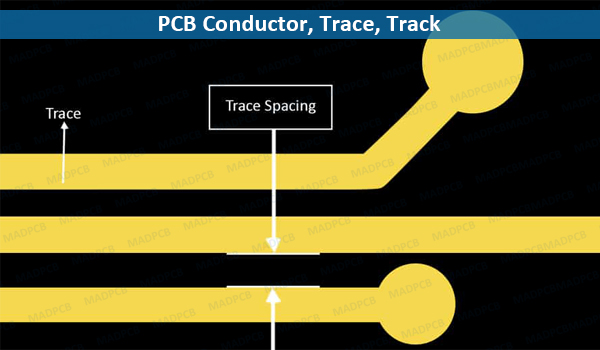
Trace Width and Spacing
Narrower traces and tighter spacing require more precise manufacturing processes, which can raise costs.
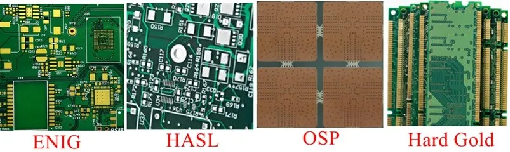
Surface Finish
Different surface finishes (e.g., HASL, ENIG) have varying costs associated with them. Some finishes are more expensive but provide better perfo.
Volume and Order Size
Larger prucodtion runs typically reduce the per-unit cost due to economies of scale, while small batches may be more expensive on a per-board basis.
Manufacturing Process
The complexity of the manufacturing process (e.g., automated vs. manual assembly) can impact costs. Processes that require more labor or specialized equipment tend to be pricier.
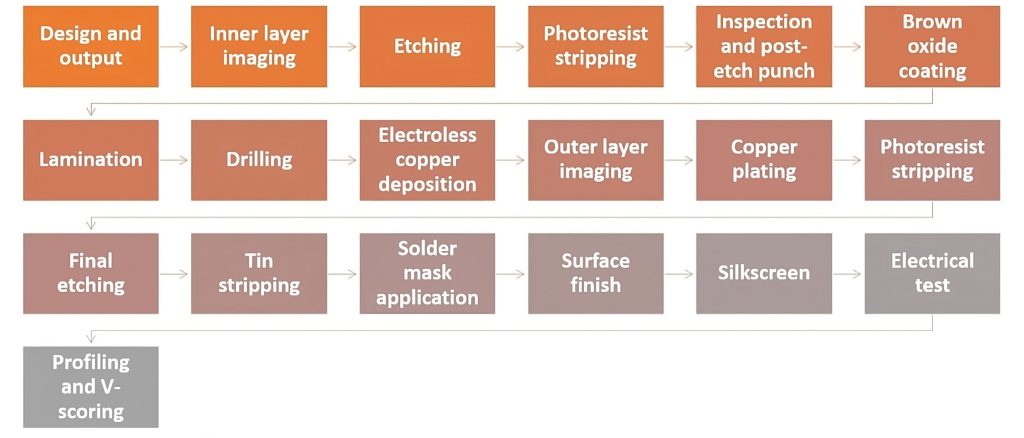
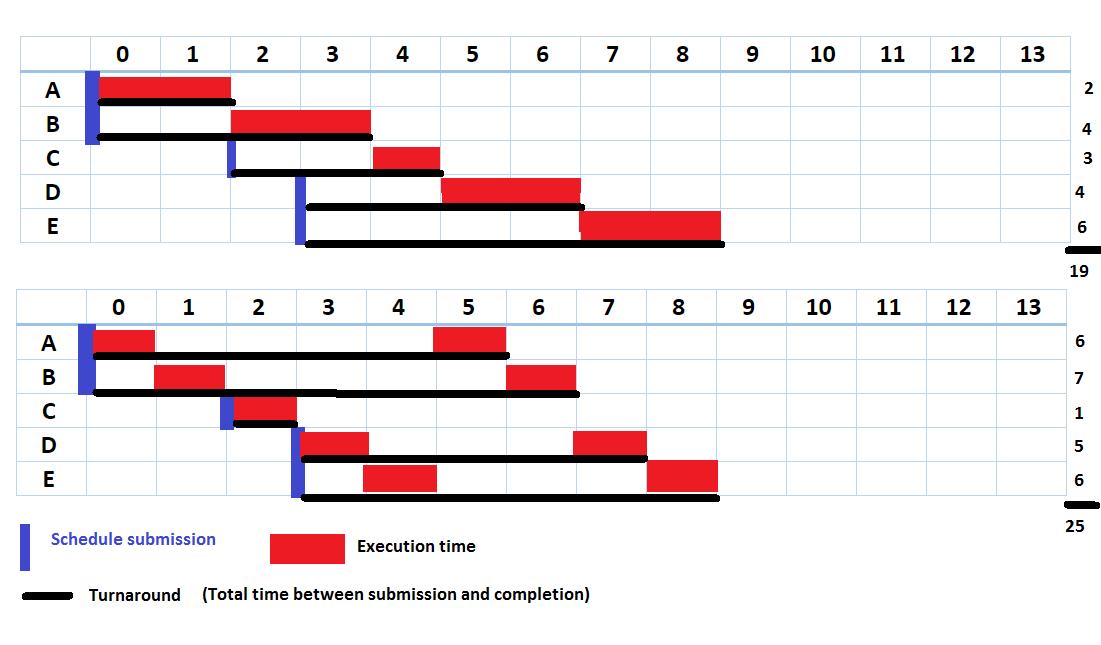
Turnaround Time
Expedited production services often come with a premium. Standard lead times are more cost-effective.
Design Complexity
Complex designs that require advanced manufacturing techniques (like blind/buried vias or high-density interconnections) can increase costs.
Testing and Inspection
Additional testing procedures (e.g., electrical testing, X-ray inspection) can add to the overall price of the PCB.
Shipping and Logistics
Costs associated with shipping, especially for international orders, can affect the overall price.

Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with industry standards (e.g., RoHS, IPC) may necessitate additional processes, influencing costs.
By understanding these factors, you can make more informed decisions when budgeting for PCB production.

Or call +86 755 2794 4155
Inquiry Now

